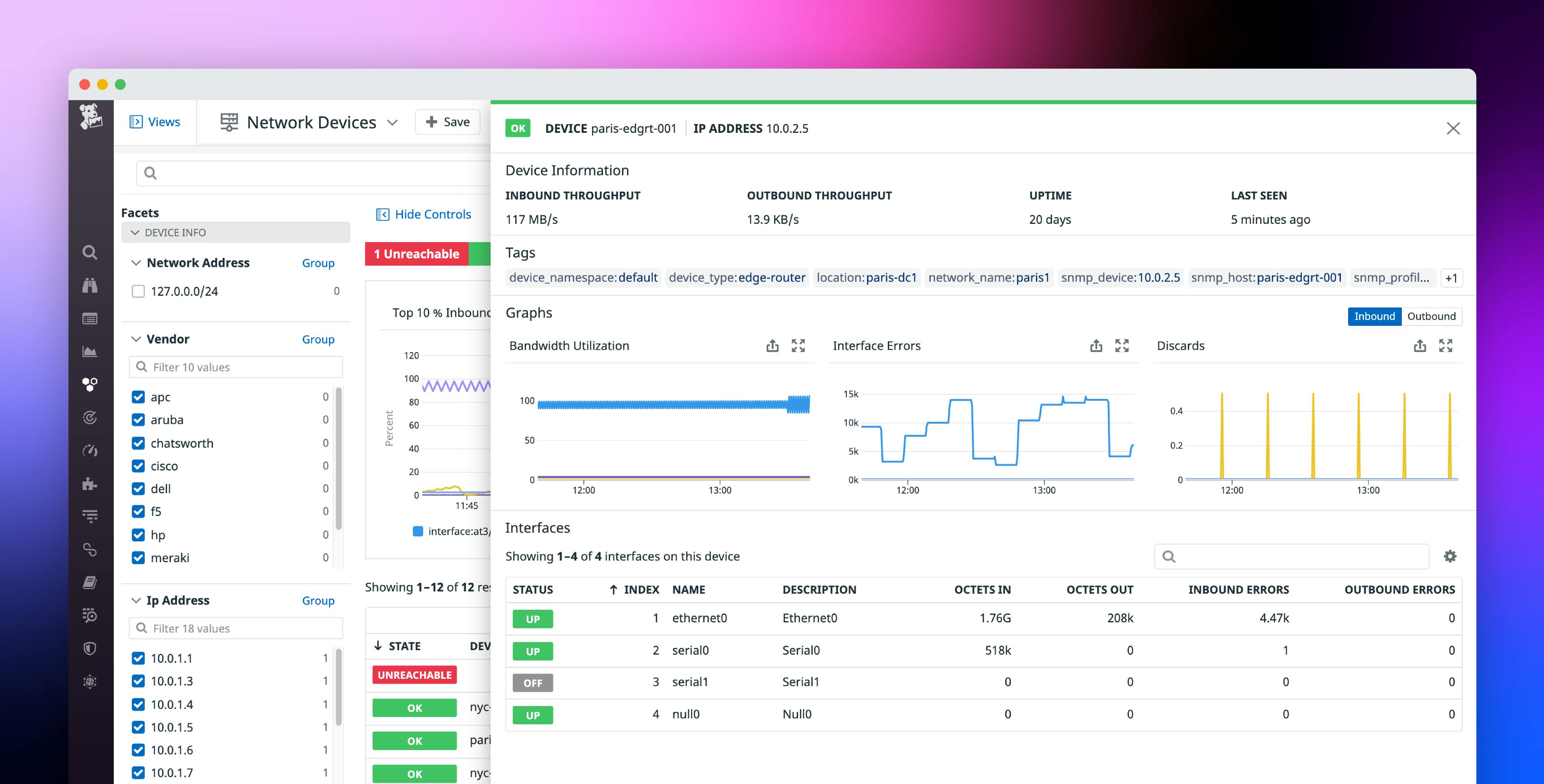
Network Device Monitoring: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
Introduction
Network device monitoring is the process of tracking and analyzing the performance and health of your network devices. This includes routers, switches, firewalls, and servers. By monitoring your network devices, you can identify and resolve problems before they impact your users.
Why is network device monitoring important?
Network device monitoring is important for several reasons:
- Improved Performance: By monitoring your network devices, you can identify performance bottlenecks and optimize your network for better performance.
- Increased Uptime: Network device monitoring can help you identify and resolve problems before they cause outages.
- Reduced Costs: By preventing outages and resolving problems quickly, you can reduce the costs associated with downtime.
- Improved Security: Network device monitoring can help you identify and respond to security threats.
- Better Planning: Network device monitoring can help you plan for future network growth.
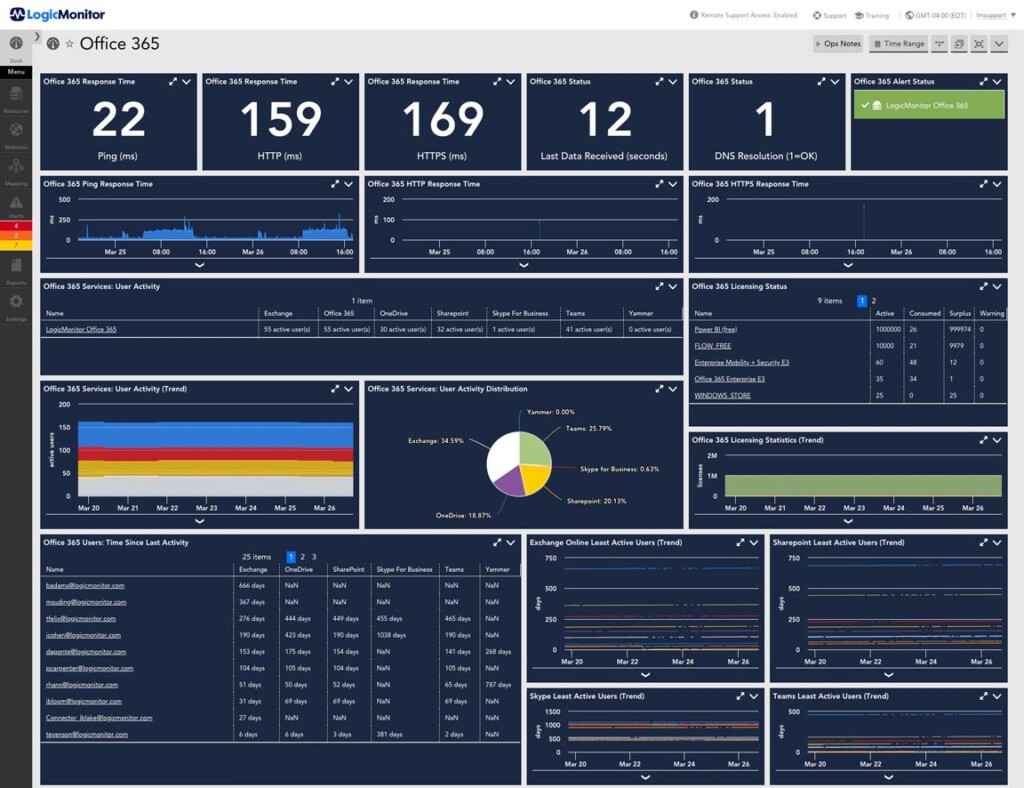
What are the benefits of network device monitoring?
The benefits of network device monitoring include:
- Proactive Problem Solving: Network device monitoring allows you to identify and resolve problems before they impact your users.
- Improved Network Efficiency: Network device monitoring can help you optimize your network for better performance.
- Reduced Downtime: Network device monitoring can help you reduce the amount of time your network is down.
- Better Security: Network device monitoring can help you identify and respond to security threats.
- Improved Planning: Network device monitoring can help you plan for future network growth.

How does network device monitoring work?
Network device monitoring works by collecting data from your network devices and analyzing that data to identify problems. This data can include things like CPU utilization, memory usage, and network traffic.
What are the different types of network device monitoring?
There are several different types of network device monitoring, including:
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP): SNMP is a protocol that is used to collect data from network devices.
- NetFlow: NetFlow is a protocol that is used to collect network traffic data.
- Syslog: Syslog is a protocol that is used to collect log data from network devices.
- Performance Monitoring: Performance monitoring involves collecting data on the performance of your network devices.
- Security Monitoring: Security monitoring involves collecting data on the security of your network devices.
What are the different tools for network device monitoring?
There are many different tools available for network device monitoring. Some popular tools include:
- Nagios: Nagios is a popular open-source network monitoring tool.
- Zabbix: Zabbix is another popular open-source network monitoring tool.
- SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor: SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor is a commercial network monitoring tool.
- ManageEngine OpManager: ManageEngine OpManager is another commercial network monitoring tool.
- PRTG Network Monitor: PRTG Network Monitor is a commercial network monitoring tool.
Table 1: Comparison of Network Monitoring Tools
| Feature | Nagios | Zabbix | SolarWinds NPM | ManageEngine OpManager | PRTG Network Monitor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open Source | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Cost | Free | Free | Paid | Paid | Paid |
| Ease of Use | Moderate | Moderate | Easy | Easy | Easy |
| Features | Extensive | Extensive | Extensive | Extensive | Extensive |
| Scalability | Good | Good | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
Choosing the right network device monitoring tool
When choosing a network device monitoring tool, you need to consider your specific needs and requirements. Some factors to consider include:
- Your budget: Some tools are free, while others are paid.
- The size of your network: Some tools are better suited for small networks, while others are better suited for large networks.
- The features you need: Some tools offer more features than others.
- Your technical skills: Some tools are easier to use than others.
Implementing network device monitoring
Implementing network device monitoring involves several steps:
- Identify your network devices: The first step is to identify all of the network devices on your network.
- Choose a monitoring tool: The next step is to choose a monitoring tool that meets your needs.
- Install the monitoring tool: Once you have chosen a monitoring tool, you need to install it on a server.
- Configure the monitoring tool: Once the monitoring tool is installed, you need to configure it to monitor your network devices.
- Monitor your network devices: Once the monitoring tool is configured, you can start monitoring your network devices.
Analyzing network device monitoring data
Once you have collected data from your network devices, you need to analyze that data to identify problems. This can be done manually or by using automated tools.
Responding to network device monitoring alerts
When a network device monitoring tool detects a problem, it will typically generate an alert. You need to respond to these alerts promptly to prevent problems from escalating.
Keywords: Network device monitoring, network monitoring tools, SNMP, NetFlow, Syslog, Nagios, Zabbix, SolarWinds, ManageEngine, PRTG, network performance, network security, network uptime, network troubleshooting, network management.
Conclusion
Network device monitoring is essential for maintaining a healthy and efficient network. By monitoring your network devices, you can proactively identify and resolve problems, improve network performance, and reduce downtime. There are many different tools available to help you monitor your network devices, so it’s important to choose a tool that meets your specific needs and requirements. Remember that effective monitoring is not just about the technology; it’s about establishing clear processes for alert response and ongoing network optimization.
FAQ
- Q: What is the difference between network device monitoring and network performance monitoring?
A: Network device monitoring is a broader term that encompasses all aspects of monitoring your network devices, including performance. Network performance monitoring is a specific type of network device monitoring that focuses on the performance of your network devices.
- Q: How much does network device monitoring cost?
A: The cost of network device monitoring can vary depending on the tool you choose. Some tools are free, while others can cost thousands of dollars per year.
- Q: How long does it take to implement network device monitoring?
A: The time it takes to implement network device monitoring can vary depending on the size of your network and the complexity of your monitoring requirements. It can range from a few hours to several weeks.
- Q: What are some common network device monitoring metrics?
A: Some common network device monitoring metrics include CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, network traffic, and error rates.
- Q: How can I improve the accuracy of my network device monitoring?
A: You can improve the accuracy of your network device monitoring by ensuring that your monitoring tools are properly configured and that you are collecting data from all of your network devices.
Table 2: Common Network Device Monitoring Metrics
| Metric | Description | Units |
|---|---|---|
| CPU Utilization | The percentage of CPU time that is being used. | Percentage (%) |
| Memory Usage | The amount of memory that is being used. | Megabytes (MB) |
| Disk Space | The amount of disk space that is available. | Gigabytes (GB) |
| Network Traffic | The amount of data that is being transmitted over the network. | Bits per second (bps) |
| Error Rates | The number of errors that are occurring on the network. | Errors per second |
| Packet Loss | The percentage of packets that are being lost on the network. | Percentage (%) |
| Latency | The delay in transmitting data over the network. | Milliseconds (ms) |
| Jitter | The variation in latency. | Milliseconds (ms) |
| Uptime | The amount of time that a device has been running without interruption. | Hours/Days |
This expanded article provides a more in-depth look at network device monitoring, incorporating tables, FAQs, and a more conversational tone suitable for an 8th or 9th-grade reading level. Remember to always adapt the complexity to your specific audience.